Geo Router (Proxy)
Technical Specifications
| Latest release |
2.39 ,
30 May 2023 ,
[Change Log, Previous Releases]
|
| Supported networking |
Ethernet, IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP. |
|
Traffic routing engine
|
Kernel-mode network driver. |
| Prerequisites |
.NET 4.5.2, up-to-date root certificates (otherwise, startup may be delayed
by up to 2 minutes).
|
| Supported OSes |
Windows 7*, 8, 8.1, 10, 11, Server 2008 R2*, Server 2012, Server 2012 R2,
Server 2016, Server 2019, and Server 2022.
*For Windows 2008 R2 and 7, required Service Pack 1 +
KB3033929
(SHA-2 digital signing).
*For Windows 8.1 and Server 2012 R2,
KB2995730 is required.
|
| Recommended hardware |
1 GHz CPU or faster, modern graphics card. |
| Additional hardware required |
None. |
Overview
Geo Router acts as a reverse proxy, splitting incoming traffic by country of origin and
routing it to specified servers. At its core, Geo Router uses a device driver for
traffic routing, ensuring minimal latency.
In routing, Geo Router hides the IP addresses of the communicating parties, using its
own IP address for communication. To external parties, it appears that they are
communicating directly with the Geo Router system.
Standard proxies require at least two network cards. Geo Router works with a single
network card having a single IP address. It automatically detects the hardware configuration and
configures itself to route traffic to the specified targets. It can also be part of a
routing chain where more specific rules are applied at each hop.
Here are the most common scenarios for Geo Router.
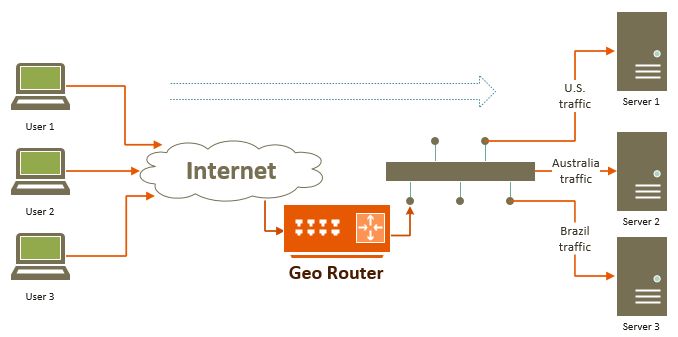
Geo Router with two network interfaces
Geo Router with a single network interface
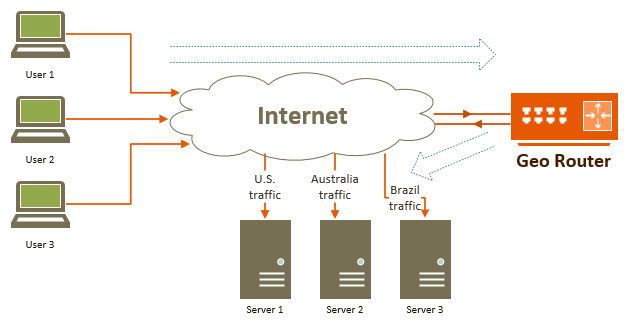
Here, Geo Router acts as a proxy server, receiving connection requests from around the
world. Internet users connecting to Geo Router are not exposed to the routing and IP
address translation happening behind the scenes. To them, Geo Router appears as a
regular server. When forwarding traffic to routing targets (servers providing the
actual content), it performs IP address translation, making the traffic appear to
originate from Geo Router by placing its own IP address on each packet. This enhances
the security of the content servers.
Geo Router
IMPORTANT: When used on a Virtual Machine, accidental rule changes may affect
Remote Desktop (RDP) traffic and lockout a user. For instructions on restoring RDP
connectivity, see our KB article:
Restoring Remote
Desktop (RDP) connectivity to an Azure VM after a user lockout.
Geo Router adds an icon to the system tray. When its main window is closed, it remains
in the system tray. To fully stop Geo Router, use the context menu of the system tray
icon.

Assigning a Routing Target
Geo Router displays assigned routing targets next to countries. All traffic from those
countries is forwarded to the associated targets. Countries without routing targets do
not have their traffic forwarded.
A routing target can be specified in the Routing Target box. It must
then be assigned to one or more geographical territories by selecting them individually
or as a region. Clicking the Assign Target button assigns the routing
target to the selected territories.
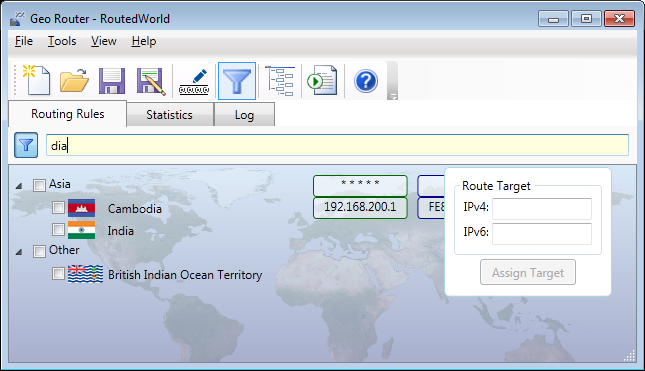
A routing target can have an IPv4 address, an IPv6 address, or both. An empty field
clears the routing target. The appropriate IPv4/IPv6 routing target is automatically
chosen during traffic processing.
Reserved IPv4/IPv6 Networks
In addition to geographical territories, Geo Router understands and works with reserved
networks. These are used by computers to communicate with other devices on local
networks. Reserved networks are found under [Reserved Networks IPv4]
and [Reserved Networks IPv6].
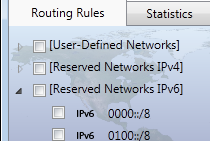
Reserved networks are predefined. While they can be routed, their definitions cannot be
edited. It is recommended not to route them to avoid unusual networking situations.
Adding User-Defined Networks
In addition to predefined geographical territories and reserved networks, Geo Router
allows you to add user-defined networks, which appear under the
[User-Defined Networks] region. User-defined networks are part of the
rules, not the program Settings, and they are saved and loaded with the rules.
To edit user-defined networks, click the
 button on the toolbar. Since IPv4 and IPv6 networks have different address formats,
they are edited separately.
button on the toolbar. Since IPv4 and IPv6 networks have different address formats,
they are edited separately.
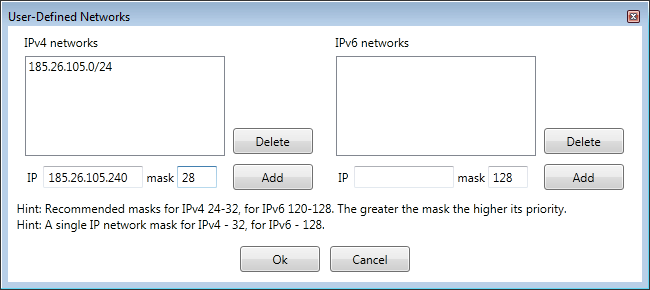
When editing, user-defined networks can overlap with other user-defined networks or
predefined geographical territories. In such cases, rule precedence determines which
rules apply. More specific networks (those with a greater network mask) always take
precedence over less specific ones.
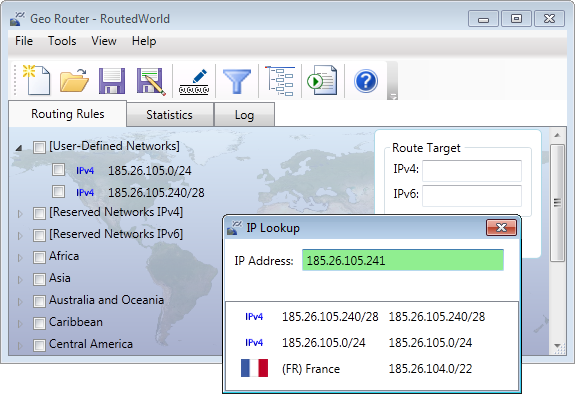
For example, the network 192.168.1.1/32 is more specific than 192.168.0.0/16; thus,
rules for 192.168.1.1/32 take precedence for traffic to 192.168.1.1.
IP Geo Lookup is a great way to determine which network rules take
precedence.
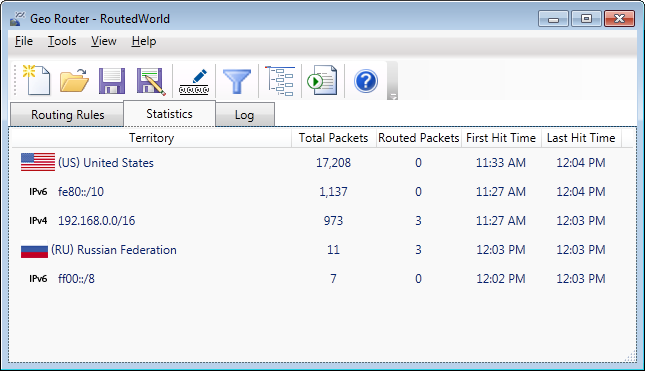
Statistics
Statistics make it easy to understand traffic destinations. Data is accumulated from
the program's start. Settings can be adjusted to include or exclude non-country
records, and an expiration interval can be set for removing inactive items. Data collection and
visualization impact CPU performance. While negligible on laptops, disabling
statistics on servers with high CPU usage and network throughput can improve
performance.
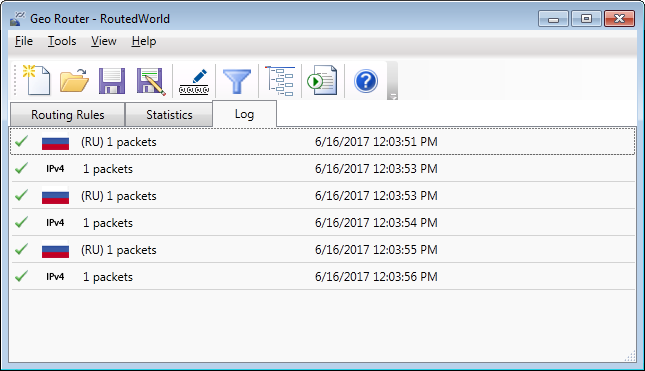
Log
Logging helps track the historical performance of rules. The refresh rate can be
adjusted in the settings. Like statistics, logging impacts CPU performance, so
disabling it can reduce CPU usage and improve performance.
Settings
Geo Router settings can be changed via the Settings dialog.
Notes:
* Windows® is a registered trademark of the
Microsoft Corporation.