Multi Port Forwarder
Technical Specifications
| Latest release |
6.53 ,
10 Dec 2024 ,
[Change Log, Previous Releases]
|
|
Supported networking
|
Ethernet, IPv4, IPv6, TCP, UDP. |
|
Traffic transformation engine
|
Kernel-mode network driver. |
| Prerequisites |
.NET 4.5.2, up-to-date root certificates (otherwise, startup may be delayed
by up to 2 minutes).
|
| Supported OSes |
Windows 7*, 8, 8.1, 10, 11, Server 2008 R2*, Server 2012, Server 2012 R2,
Server 2016, Server 2019, and Server 2022.
*For Windows 2008 R2 and 7, required Service Pack 1 +
KB3033929
(SHA-2 digital signing).
*For Windows 8.1 and Server 2012 R2,
KB2995730 is required.
|
| Recommended hardware |
1 GHz CPU or faster, modern graphics card. |
| Additional hardware required |
None. |
Overview
This is a Swiss Army knife of port forwarding, transforming network traffic in any
way imaginable. Traffic for forwarding is selected by a combination of direction
(incoming/outgoing), protocol (TCP/UDP), port, IP (IPv4, IPv6, DNS name), MAC, and
network interface. Any of these can be selected together or individually. The program
goes beyond forwarding, offering traffic reflection back to the source on a local or
remote computer, with or without transposing addresses. An activity indicator for each
rule conveniently shows the traffic being processed. The program provides high
performance and efficient resource use, even on older operating systems.
What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding is similar to network address translation (NAT) but only translates
port numbers. To illustrate, two computers on the Internet communicating via TCP or
UDP use ports to identify each other's connection points. To communicate, each
computer must know the other's port and IP address to send data to that port. Multi
Port Forwarder forwards these ports so that when one computer sends data to a specific
port, the data is transparently sent to a different one. Applications are unaware of this
forwarding.
An example scenario for incoming traffic: When a remote computer sends traffic to the
specific port on local computer (e.g., HTTP port 80), Multi Port Forwarder can
forward local port 80 to a port specified in the rules (e.g., port 8080). This allows
the local server to listen on port 8080 and receive data sent to port 80.
Working with Multi
Port Forwarder
IMPORTANT: When used on a Virtual Machine, accidental rule changes may affect
Remote Desktop (RDP) traffic and lockout a user. For instructions on restoring RDP
connectivity, see our KB article:
Restoring Remote
Desktop (RDP) connectivity to an Azure VM after a user lockout.
Multi Port Forwarder's actions are rule-based. Rules can be added or removed using
the toolbar buttons or the menu and can be enabled or disabled with a checkbox. They
take effect with a delay that is configurable in the Settings.
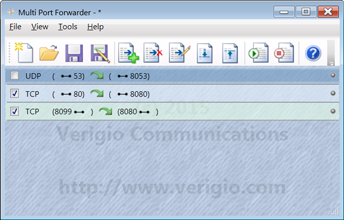
Rules are executed from top to bottom. The first rule that matches the network traffic
is executed, and no other rules are processed for that traffic.
Rule editing has been significantly simplified compared to previous versions. The
interface now operates in terms of Local and Remote addresses. Checkboxes allow
individual selection of parameters for traffic selection and modification.
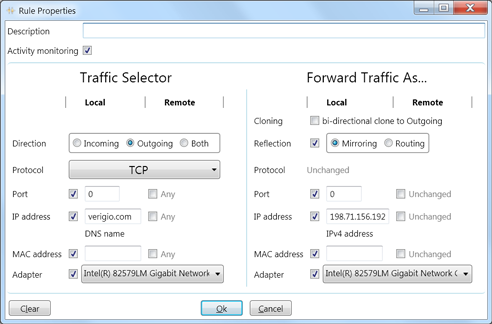
-
Description - A description or title for the rule, which is
displayed in the rules list.
-
Activity monitoring - Enables a yellow, LED-like indicator in the
rules list to flash when the rule is triggered.
-
Traffic Selector section - Parameters for selecting the traffic to
be modified.
-
Forward Traffic As... section - Parameters for the traffic
modification.
Traffic Selector
-
Direction - The direction of the first packet that triggers
the rule. When the first packet is processed, a bi-directional conversation channel
is created internally. Subsequent packets for the same conversation can go in either
direction. The channel's duration (an inactivity timeout) can be set in
Options for both TCP and UDP. Once it expires, the channel closes,
and a new rule matching packet is needed to create it again.
- Protocol - UDP or TCP.
- Port - A port number from 1 to 65535.
-
IP address - An IPv4 or IPv6 address, or a DNS name. The hint below
displays the identified entry type. When a DNS name is used, it is resolved to a list
of IP addresses, and all associated IP addresses are
used. DNS resolution occurs once when the rules are run; there is
no continuous monitoring of DNS name associations.
-
MAC address - The MAC address. NOTE: All traffic arriving at a
computer has the local MAC address of its network card or a broadcast/multicast
address.
- Adapter - A list of available network adapters.
Forward Traffic As...
-
Reflection - A flag that forces traffic to be sent back to its
source. If the traffic is outgoing, it will be returned; if it is incoming, it will
be sent back out.
-
Mirroring reflection - A flag that sends traffic back to its
source, preserving all Local and Remote addresses. This means the Source and
Destination addresses in each packet are transposed, but the TCP SeqNo/AckNo are
unaffected.
-
Routing reflection - A flag that sends traffic back to its
source with all Local and Remote addresses transposed. This means the Source and
Destination addresses of each packet will not change. Routing is performed after
all other changes are made.
- Port - A port number from 1 to 65535.
-
IP address - An IPv4 or IPv6 address, or a DNS name. The hint below
displays the identified entry type. When a DNS name is used, it is resolved to a list
of IP addresses, and only the first associated IP
address is used. DNS resolution occurs once when the rules are run; there is
no continuous monitoring of DNS name associations.
-
MAC address - The MAC address. NOTE: For the recipient to communicate
with the source, the Local MAC address must be that of the network card sending the
traffic.
- Adapter - A list of available network adapters.
Examples
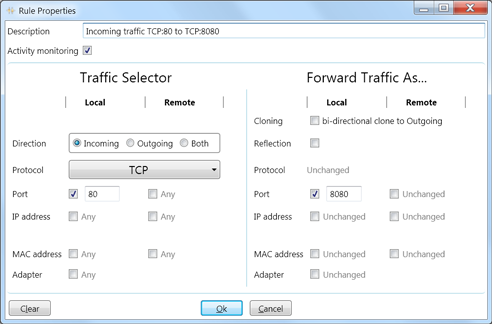
Example #1
Forward all incoming traffic from TCP port 80 to port 8080.
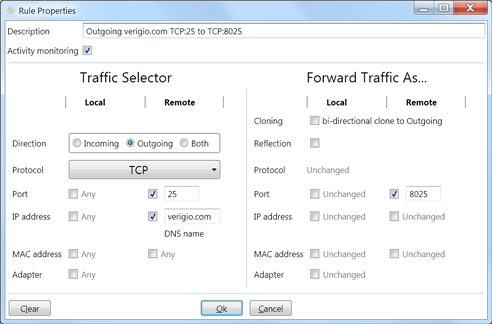
Example #2
Forward outgoing traffic for verigio.com from TCP:25 to TCP:8025.
Example #3
Monitor web traffic activity (without making changes).
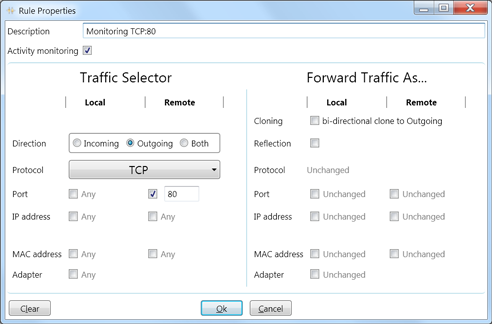
Monitoring will start when the local computer connects to a remote web server and will be
performed in both directions (even though the Direction is set to Outgoing), as a
bi-directional communication channel is created internally.
Example #4
Route traffic for verigio.com via a specific network adapter.
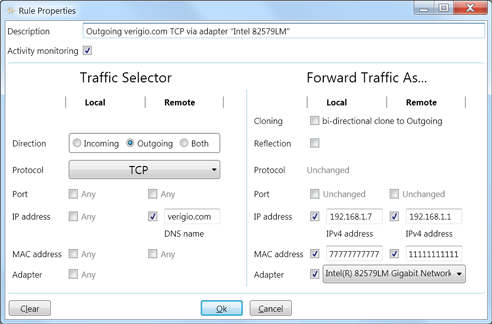
The "Forward Traffic As..." section has the following items:
-
Local IP address - The IP address associated with the network adapter. Use
"ipconfig /all" to obtain it.
-
Remote IP address - The IP address of the default gateway. Use "ipconfig /all" to
obtain it.
-
Local MAC address - The MAC address of the local network adapter. Use "ipconfig /all"
to obtain it.
-
Remote MAC address - The MAC address of the default gateway's network adapter. Use
"ping 'Remote IP address'" then "arp -a" to obtain it.
Example #5
Route all incoming web traffic (TCP:80) to another server (192.168.1.8 TCP:8080).
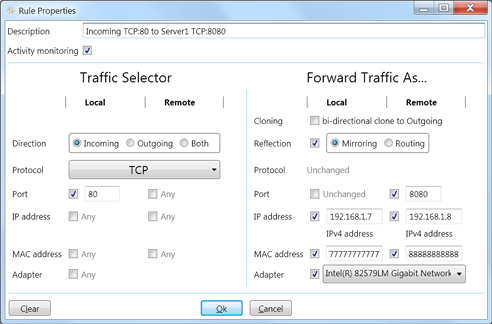
The "Forward Traffic As..." section has the following items:
-
Reflection - Mirroring reflection preserves Local and Remote addresses without
changes (the source and destination addresses for each packet will, of course, be
transposed).
- Remote Port - The listening port on the remote server.
-
Local IP address - The IP address associated with the network adapter. Use
"ipconfig /all" to obtain it.
-
Remote IP address - The IP address of the other server. Use "ipconfig /all" to
obtain it.
-
Local MAC address - The MAC address of the local network adapter. Use "ipconfig /all"
to obtain it.
-
Remote MAC address - The MAC address of the other server's network adapter. Use
"ping 'Remote IP address'" then "arp -a" to obtain it.
Third-Party Tools for Network Debugging
Notes:
* Windows® is a registered trademark of the
Microsoft Corporation.